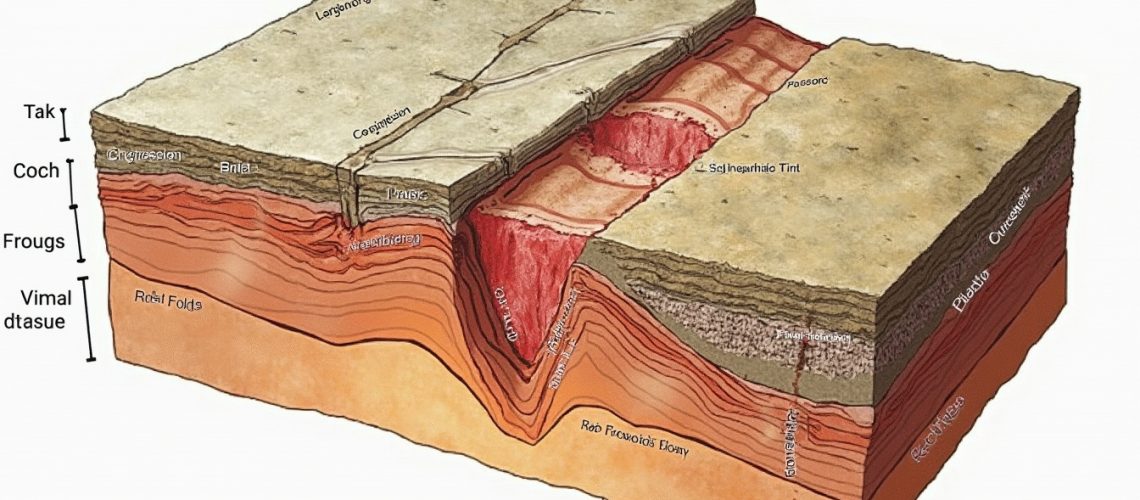
Rock deformation is a complex geological process that reveals the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. This fundamental mechanism describes how rocks change shape, volume, or position in response to applied stress, providing critical insights into the planet’s structural evolution and tectonic activity.
What Is Rock Deformation and Why Is It Important?
Rock deformation occurs through various mechanisms that fundamentally shape our understanding of geological processes. It is estimated that over 70% of the Earth’s surface experiences some form of rock deformation due to tectonic activity, making it a crucial area of scientific investigation.
At its core, rock deformation helps researchers understand how tectonic activity influences the Earth’s geological structures. The process is critical for multiple disciplines, including resource exploration, seismology, and understanding geological hazards.
How Do Different Types of Stress Cause Rock Deformation?
Stress represents the primary driving force behind rock deformation, manifesting in three primary types:
- Compression: Forces pushing rocks together, causing shortening and thickening.
- Tension: Forces pulling rocks apart, resulting in stretching and thinning.
- Shear: Forces acting parallel but in opposite directions, causing rocks to distort.
These stress types are particularly evident in examples like transform boundaries, where tectonic plates interact and generate complex geological structures.
What Are the Different Types of Rock Deformation?
Rock deformation can be categorised into three primary types:
- Elastic Deformation: Temporary shape changes that revert once stress is removed.
- Plastic/Ductile Deformation: Permanent deformation without fracturing, typically occurring at high temperatures and pressures.
- Brittle Deformation: Rock fracturing when stress exceeds its structural strength.
What Factors Influence Rock Deformation?
Several critical factors determine how rocks respond to stress:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase ductility
- Pressure: Increased pressure promotes plastic deformation
- Rock Type: Mineral composition affects deformation characteristics
- Strain Rate: Speed of stress application impacts deformation type
Where Does Rock Deformation Typically Occur?
Rock deformation predominantly occurs in dynamic tectonic settings:
- Convergent Boundaries: Characterized by compressive stress and mountain building
- Divergent Boundaries: Associated with tensional stress and rift valley formation
- Transform Boundaries: Featuring shear stress and strike-slip faulting
Why Is Understanding Rock Deformation Important?
Understanding rock deformation provides crucial insights for multiple disciplines:
- Engineering geology: Designing stable structures
- Seismology: Predicting earthquake potential
- Resource Exploration: Identifying mineral deposit formations
- Tectonic Research: Reconstructing geological history
What Are Some Notable Examples of Rock Deformation?
Prominent examples include:
- The Himalayas: Formed by compressive stress between Indian and Eurasian plates
- East African Rift Valley: Demonstrating tensional stress
- San Andreas Fault: Illustrating shear stress and transform boundary dynamics
Conclusion: The Significance of Rock Deformation
Rock deformation represents a fundamental process that continually reshapes our planet. By understanding its mechanisms, researchers can better predict geological phenomena, assess natural hazards, and unlock the Earth’s complex geological history.
Through careful analysis of stress types, deformation mechanisms, and influencing factors, scientists continue to unravel the intricate processes that have sculpted our planet’s remarkable landscape over millions of years.
How Can Understanding Rock Deformation Enhance Your Investment Strategy?
Uncover the latest in geological analysis and investment opportunities with Discovery Alert’s real-time notifications. Our AI-powered service simplifies complex data, transforming it into actionable insights for both new and seasoned investors. Tap into the world of significant ASX mineral discoveries and stay ahead of the market. Experience it firsthand with a 30-day free trial at Discovery Alert.